The term Glastobioma has recently started gaining attention across scientific, environmental, and health-related discussions. While it may sound complex at first, Glastobioma represents a fascinating intersection of biology, ecosystems, and innovative technology. Whether you’re a student, researcher, or simply curious about future-oriented sciences, learning about Glastobioma can give you valuable insights into how natural systems and advanced research converge.
In this guide, we’ll break down the meaning of Glastobioma, its applications, benefits, and potential challenges. We’ll also explore frequently asked questions to give you a complete overview in simple, easy-to-digest language.
What Is Glastobioma?
At its core, Glastobioma refers to a biological framework or system where ecosystems, microorganisms, and technological innovations interact to create sustainable solutions. Think of it as a fusion between glass-like controlled environments and biomes (natural living systems).
- Glass → Symbolizes transparency, laboratory conditions, or greenhouse-like ecosystems.
- Biome → Refers to a natural community of plants, animals, and microbes.
By combining these ideas, Glastobioma focuses on studying controlled ecosystems to better understand biodiversity, sustainability, and potential applications in medicine, agriculture, and environmental management.

The Origins of Glastobioma
While the exact origin of the term is still debated, researchers suggest that Glastobioma emerged as a scientific concept linking:
- Microbiomes (the communities of microorganisms in a given environment).
- Glass-controlled environments (such as greenhouses, laboratories, or biospheres).
- Sustainability research aiming to balance human progress with ecological preservation.
In short, Glastobioma is not just a buzzword—it’s a forward-looking field of study combining biology and technology.
Why Is Glastobioma Important?
The significance of Glastobioma lies in its practical applications across multiple industries.
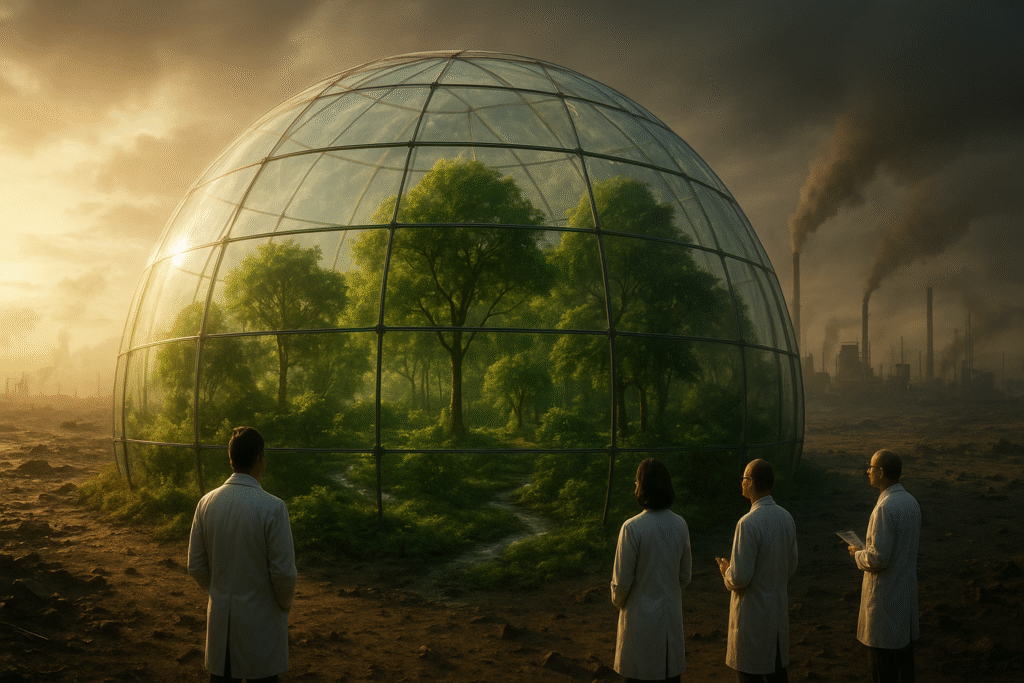
1. Environmental Science
Glastobioma can help scientists design closed-loop ecosystems, reduce waste, and create renewable environments that mimic nature.
2. Medicine and Healthcare
By studying microorganisms within controlled biomes, Glastobioma research can lead to better probiotics, disease prevention, and gut health treatments.
3. Agriculture and Food Security
Imagine growing crops in self-sustaining glass ecosystems where plants, soil microbes, and water cycles interact naturally. Glastobioma could make this a reality.
4. Climate Change Solutions
Glastobioma models can simulate how ecosystems respond to temperature, CO₂, and pollution, offering predictive data for climate resilience.
Key Components of Glastobioma
To better understand the concept, let’s break it down into three main pillars:
1. Microbial Communities
These are the tiny life forms—bacteria, fungi, and protozoa—that play a massive role in soil health, human wellness, and global ecosystems.
2. Controlled Environments
Glastobioma emphasizes glass-contained ecosystems such as:
- Biospheres
- Greenhouses
- Aquaponics systems
3. Human Interaction
Humans interact with Glastobioma by studying, experimenting, and applying its principles in real-world solutions.
Applications of Glastobioma in Everyday Life
Here’s where things get exciting—Glastobioma is not just theoretical. It has real-world uses already shaping industries.
Agriculture and Food Production
- Enhanced soil microbiomes for healthier crops.
- Reduced reliance on chemical fertilizers.
- Sustainable farming models inside glass-controlled ecosystems.
Healthcare and Medicine
- Studying human gut microbiomes in controlled glass-like environments.
- Developing new therapies, probiotics, and treatments for chronic diseases.
Environmental Sustainability
- Designing miniature self-sustaining ecosystems for urban spaces.
- Recycling water and nutrients naturally.
- Improving carbon capture through ecosystem modeling.
Space Exploration
NASA and other space agencies are interested in biospheres and biomes under glass domes to support life on Mars or the Moon. Glastobioma could be key to extraterrestrial survival.
Benefits of Glastobioma
Why should we care about Glastobioma? Because it offers multiple benefits across science, society, and nature:
- Sustainability: Encourages eco-friendly solutions.
- Health advancements: Unlocks new ways to support human microbiomes.
- Resilience: Helps predict and mitigate climate change effects.
- Innovation: Creates opportunities for biotech, agriculture, and medical startups.
Challenges of Glastobioma
Like any emerging field, Glastobioma faces hurdles.
- Complexity: Ecosystems are highly dynamic and hard to replicate.
- Cost: Creating and maintaining glass biomes is expensive.
- Ethics: Manipulating natural systems raises moral questions.
- Scalability: Can small experimental models be applied on a global level?
Future of Glastobioma
The future looks promising. With ongoing research, we can expect:
- Smarter biomes powered by artificial intelligence.
- Integration with nanotechnology for precision control of microorganisms.
- Eco-cities where Glastobioma-inspired ecosystems are built into architecture.
- Space colonization supported by glass-contained biomes.
In essence, Glastobioma has the potential to redefine how humans interact with nature in the 21st century and beyond.
People Also Ask: Glastobioma FAQs
1. What does Glastobioma mean in simple terms?
Glastobioma is a concept where controlled glass environments are used to study and replicate natural ecosystems for research and sustainability.
2. How is Glastobioma different from a greenhouse?
While a greenhouse focuses mainly on plant growth, Glastobioma includes microorganisms, water cycles, and entire ecosystems, making it more holistic.
3. Can Glastobioma help fight climate change?
Yes, by creating sustainable ecosystems and studying how nature reacts to stress, Glastobioma can offer insights for climate resilience.
4. Is Glastobioma used in space research?
Absolutely. Scientists are exploring biosphere-style systems to support human life on Mars and other planets.
5. What industries will benefit most from Glastobioma?

- Agriculture
- Medicine
- Environmental science
- Biotechnology
- Space exploration
Conclusion
Glastobioma is more than just a scientific term—it’s a vision of the future where humans and ecosystems coexist in harmony. By combining glass-contained environments, microbiomes, and sustainable practices, this emerging concept has the power to transform agriculture, healthcare, climate science, and even space exploration.
As research progresses, Glastobioma could become one of the most innovative tools for building a sustainable future. Whether you’re a scientist, student, or eco-conscious individual, keeping an eye on Glastobioma is worth your time.
Another Topic To Read Winobit3.4 Software Error Quick Fixes, Causes, and Prevention Guide






